30/03/20
Q&A: Recovering from war with help from space

Send to a friend
The details you provide on this page will not be used to send unsolicited email, and will not be sold to a 3rd party. See privacy policy.
自从Sputnik 1推出以来,卫星已被用来从空间的独特风格中检查我们的星球。从诸如臭氧洞之类的大科学发现到日常天气预报,太空技术已经改变了我们对地球自然过程的理解。
Images also track humanity’s transformation of landscapes: growing cities, altered waterways and effects of conflict. Improvements in optical and sensing technology, paired with artificial intelligence, mean that today’s satellites are already being leveraged to improve the lives and livelihoods of billions around the world.
实际上,卫星图像已习惯进步many of the global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), saysBertrand Frot, information management specialist with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). A 2016pilot programme根据Frot的说法,在马里廷巴克图古城的战争重建工作中,有一个明显的教训,据Frot说:“卫星数据很容易。一切都很明显。”
How did the Mali work inform the UNDP’s decision to invest more deeply in satellite imagery for disaster response, reconstruction and development?
One image is worth 100 pages of a report from the ground.
进入某些地区仍然很困难 - 许多地区的地雷炸毁了道路。您可以看到每个图像的环境影响 -beplay足球体育的微博 河流接触Timbuktu,建筑物和基础设施的重建的进展,市场规模的发展。您还可以看到仍然被破坏的东西。
在受战争影响的其他领域,我们已经开始培训人们恢复农业以及战争如何影响环境。beplay下载官网西西软件beplay足球体育的微博在伊拉克,许多树木被摧毁,因为射手可以躲在他们身后。因此,现在风可以从南到北部更容易地携带沙子,并且它确实改变了城市的景观和农业。beplay下载官网西西软件对历史和当前卫星数据的分析可以向我们展示针对恢复工作的何处,或建立新的基础设施来保护农作物,或者是开发新农田的最佳领域。
Are there any SDGs that might particularly benefit from greater use of space technology or AI data processing?
Poverty is the main one. Towards zero hunger, satellite data is being used to evaluate droughts and agricultural yields. Economic growth — the evolution of cities and poverty within cities, as well as how industry and infrastructure are evolving in those places — this is directly related to the SDG to reduce inequality: images can be used to evaluate the evolution of rural and urbanized areas, where in many cases the slums are really visible.
气候行动,大多数certainly. TheSpace Climate Observatory提供开源数据,并允许对全球气候变化的影响进行大量国际研究。
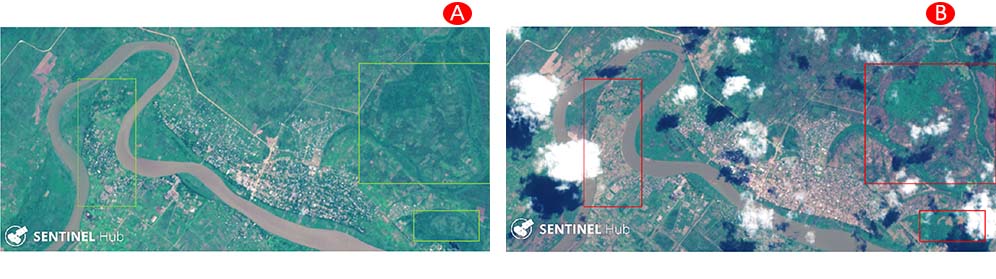
One area your office says satellite imagery can help with is getting resources to those who need it most. How does that actually work?
We’ve used this type of analysis in cities like Casablanca, Cairo, Djibouti and in Nigeria. It helps with the planning and evolution of public services.
In Nigeria, we were able to correlate the evolution of some cities with interviews done with migrants who had arrived in Europe from these areas. And then we could take that information to the local Nigerian authorities and say: your area is a large source of migration. Which can help them plan the extensions of their cities and its services more effectively.
您的办公室还在印度尼西亚工作,探索洪水及其对水稻种植的影响。这种知识如何转化为农民的行动?
This relates to impacts from climate change. There are some areas where there is less rain over the year, but more concentrated rainfall events that flood the rivers more often than before. Here, satellite data was helpful in seeing the impact of the floods on the supply chain. If silos and warehouses are located in flood zones, or their access roads are inundated, the rice can’t be moved. So these data help in repositioning roads and bridges, or for locating structures to protect the crops.
In Kenya, there are some areas that are regularly flooded, and in some areas new roads can be built to use as a barrier to protect from floods. The imagery helps evaluate whether those barriers are effective.
Are there any environmental projects that have benefited from higher-resolution satellite data?
In South America, we are working in some countries on deforestation, to monitor primary and secondary forest. The idea is to better protect biodiversity by working back towards a more complete landscape.
在乌干达,正在用卫星监测湿地恢复工作,以及导致的水质变化,并将这些变化与生计指标相关联。该项目影响了超过400万人,其中一部分正在使农民远离破坏农作物。
Is there a danger of overpromising on what satellite data can deliver?
真正的赌注在于如何将其扩展,并将其变成工业视野。我们没有什么都没有用卫星覆盖地球。因此,在这里可以真正利用人工智能的位置:为了帮助我们评估解决方案有效的条件,以及如果我们可以在另一个地方满足这些条件,我们可以复制相同的解决方案。
What are you excited about for the future of satellite technology and AI in development?
Beyond the AI算法that will allow us to scale up more rapidly, what is very cool to me is that the products are very visible. It’s easy to take it and say, I can apply it to this or that. Yesterday’s disasters can inform how to monitor risks to prevent future disasters. Or how to better recover after them. So there’s an extension of use cases, which is pretty majestic.
而且它是透明的。在假新闻周围飞舞的时期,有进步证明与捐助者,伴侣以及公民讨论,他们可以清楚地看到我们在当地的工作。